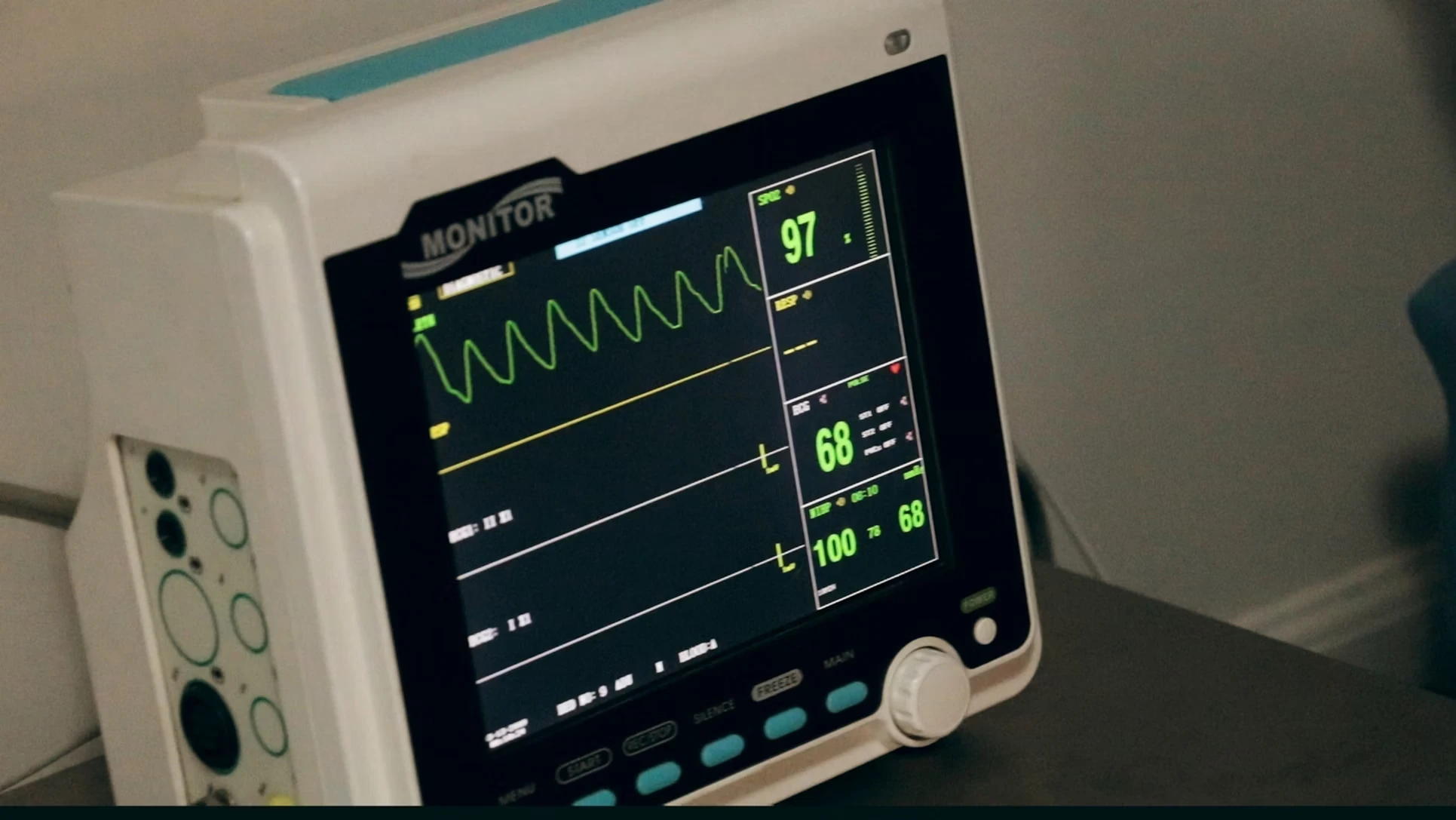
Introduction
Accurate and reliable health monitoring is fundamental to modern healthcare, enabling early detection of medical conditions, guiding treatment decisions, and ensuring that patients receive appropriate care. Whether through wearable devices, home monitoring systems, or clinical diagnostic tools, health monitoring technologies have advanced significantly, offering unprecedented insights into patient health. However, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of these monitoring systems is essential to avoid misdiagnoses, inappropriate treatments, and compromised patient safety. This article explores the critical factors, technologies, and practices involved in guaranteeing accurate and reliable health monitoring.
High-Quality Sensors and Devices
At the heart of health monitoring are the sensors and devices that collect data on various physiological parameters. From heart rate monitors and glucose meters to wearable ECGs and blood pressure cuffs, the quality of these devices is paramount. High-quality sensors must be sensitive, specific, and capable of detecting small changes in the parameters they measure. Manufacturers must adhere to stringent standards in design, materials, and calibration to ensure that these devices consistently produce accurate and reliable results. Regular maintenance, calibration, and quality checks are also necessary to maintain their performance over time.
Data Integrity and Validation
The reliability of health monitoring depends not only on the devices used but also on the integrity of the data they produce. Data integrity refers to the accuracy, consistency, and completeness of the data from the point of collection through to its analysis and storage. Ensuring data integrity involves implementing robust validation processes, including cross-checking data with other sources, applying quality control measures, and using error-detection algorithms. Data validation ensures that any anomalies or inaccuracies are identified and corrected before they can impact clinical decisions.
Calibration and Maintenance
Regular calibration and maintenance of health monitoring equipment are crucial for ensuring ongoing accuracy and reliability. Calibration involves adjusting the device to match a known standard or reference point, ensuring that its measurements are accurate. For instance, blood glucose meters must be regularly calibrated against laboratory-grade equipment to ensure their readings are precise. Maintenance, such as cleaning, battery replacement, and software updates, helps to keep the devices in optimal working condition and extends their lifespan, reducing the risk of malfunction or inaccurate readings.
Standardization and Compliance with Regulatory Guidelines
Health monitoring devices and systems must comply with industry standards and regulatory guidelines to guarantee their accuracy and reliability. Organizations such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) set standards for the design, testing, and performance of medical devices. Compliance with these standards ensures that devices meet the necessary criteria for accuracy, safety, and effectiveness. Standardization also facilitates interoperability between devices and systems, ensuring that data from different sources can be accurately combined and analyzed.
Continuous Monitoring and Real-Time Feedback
One of the key advancements in health monitoring is the shift from periodic to continuous monitoring. Continuous monitoring provides real-time data on a patient’s health status, allowing for immediate detection of changes and enabling timely interventions. This is particularly important for patients with chronic conditions or those in critical care. Continuous monitoring systems must be reliable, capable of functioning without interruption, and able to provide accurate data in real time. Integration with real-time feedback mechanisms, such as alerts or notifications, further enhances the reliability of these systems by ensuring that healthcare providers can respond promptly to any concerning changes.
Advanced Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
The integration of advanced analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) in health monitoring has significantly improved the accuracy and reliability of diagnoses and prognoses. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets, identifying patterns and correlations that might be missed by human observers. These tools can also predict potential health issues based on monitoring data, providing early warnings and enabling preventive measures. For example, AI can analyze ECG data to predict the likelihood of a cardiac event, allowing for early intervention. However, the reliability of AI-driven monitoring systems depends on the quality of the data used to train them and the algorithms’ ability to adapt to new information.
Patient Engagement and Education
Patient engagement is an often-overlooked factor in ensuring accurate and reliable health monitoring. Patients who are informed and engaged are more likely to use monitoring devices correctly and consistently, leading to more reliable data. Education on how to properly use devices, understand the readings, and respond to alerts is crucial. For example, patients with diabetes must be trained on how to use glucose meters correctly and interpret the results to manage their condition effectively. Moreover, patient feedback can provide valuable insights into the usability and reliability of monitoring systems, leading to further improvements.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring
The rise of telemedicine and remote monitoring has expanded access to healthcare, especially for patients in remote or underserved areas. However, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of remote health monitoring presents unique challenges. Remote monitoring devices must be robust and easy to use, with reliable communication channels for transmitting data to healthcare providers. Healthcare providers must also have protocols in place to verify the accuracy of the data received and take appropriate action when necessary. Ensuring that remote monitoring systems are integrated with other healthcare systems, such as electronic health records (EHRs), enhances their reliability and ensures a holistic view of the patient’s health.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
As health monitoring becomes increasingly digital, cybersecurity and data privacy have become critical concerns. Protecting the integrity and confidentiality of health data is essential for maintaining patient trust and ensuring the reliability of monitoring systems. Cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, secure authentication, and regular software updates, help protect against unauthorized access and data breaches. Ensuring that monitoring systems comply with data protection regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, further safeguards patient data and enhances the reliability of the monitoring process.
Conclusion
Accurate and reliable health monitoring is vital for effective healthcare delivery, providing the data needed for informed decision-making and timely interventions. By focusing on high-quality devices, data integrity, standardization, continuous monitoring, and patient engagement, healthcare providers can ensure that their monitoring systems are both accurate and reliable. As technology continues to advance, integrating AI, telemedicine, and robust cybersecurity measures will further enhance the effectiveness of health monitoring, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of care.